Benefits of Wi-Fi 6 for Healthcare Providers
An increasing number of medical devices enabled with Wi-Fi technology are entering the healthcare industry, ranging from simple applications to mission critical real-time applications. Blog outlines the market drivers for healthcare Wi-Fi networks.
Learn about market drivers for Healthcare Wi-Fi networks
A recently published Spirent eBook on the impact of COVID-19 on the Wi-Fi ecosystem discussed the effect of underlying factors such as the economy, business, government and consumer-behavior on Wi-Fi deployments and testing. While certain Wi-Fi market segments such as large public venues (LPV) and hospitality are still struggling to recover, the healthcare industry is facing altogether different challenges.
According to a recent report from Frost and Sullivan (April 2020), “Telehealth market in the US is estimated to display a staggering seven-fold growth by 2025, resulting in a five-year compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 38.2%. In 2020, the telehealth market is likely to experience a tsunami of growth, resulting in a year-over-year increase of 64.3%.”
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines Telehealth as the “delivery of health care services, where patients and providers are separated by distance. Telehealth uses ICT for the exchange of information for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases and injuries, research and evaluation, and for the continuing education of health professionals.”
“Wi-Fi 6 helps solve the different challenges the healthcare industry is facing.”
Wi-Fi has been the preferred wireless technology of choice for decades in hospitals and clinics, globally. This is primarily because Wi-Fi offers technical advantages in indoor environments, and often, it’s the most cost-effective option for healthcare providers. As a result, an increasing number of medical devices enabled with Wi-Fi technology are entering the healthcare industry each year, ranging from simple applications to mission critical real-time applications (e.g. ubiquitous access to patient medical records).
With stringent regulatory requirements such as FDA 510k certification for product introduction in the U.S., patient safety and privacy concerns (e.g. HIPAA in the U.S., GDPR in Europe), and the need to provide patient care around the clock (24/7/365), it is understandable that new technology adoption takes longer for the healthcare industry. However, the various new features and promises offered by Wi-Fi 6, are providing a great motivation for healthcare providers to think seriously about upgrading their devices and networks.
Benefits of Wi-Fi 6 for Healthcare Providers
Wi-Fi 6 offers several benefits over legacy standards such as Wi-Fi 5/4. Key features include Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) for Downlink and Uplink (DL/UL), Multi-user Multiple Input and Multiple Output (MU-MIMO) for DL/UL, Target Wake Time (TWT) among others.
Coupled with the latest security standard by the Wi-Fi Alliance (WFA) Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3) for Enterprise, Wi-Fi 6 enables healthcare providers to benefit from a reliable, efficient, and secured Wi-Fi connection for patient care and clinical workflows.
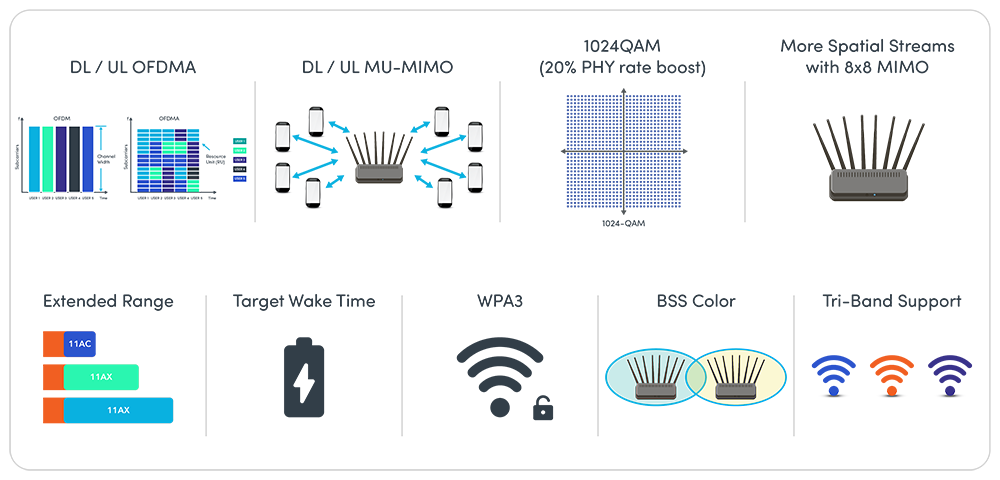
Key Wi-Fi 6 features
- OFDMA: enables higher aggregated throughput and lower latency in dense environments like in hospitals (over previous generations of products). However, the key benefit of OFDMA is the scheduling-based resource allocation capability in the frequency domain, which enables organizations to prioritize their Wi-Fi traffic. For instance, life-saving traffic data such as patient monitoring and paging can now be prioritized over less sensitive traffic such as Internet-of-Medical Things (IoMT).
- MU-MIMO: Particularly suitable for higher bandwidth applications and larger data packets, MU-MIMO (capable of up to 8×8) enables access points (APs) to transmit more data at a given time and serves a larger number of concurrent clients. Healthcare applications, ranging from full-body MRI images accessible by handheld devices to HD video for physician and patient consultation, require a higher bandwidth, that is supported by this feature.
- Target Wake Time (TWT): Large number of IoMT devices run on battery power. With TWT, APs and IoMT devices can “wake up” at negotiated times. In multiple WLANs deployment scenarios in congested environment like hospitals and clinics, this allows for reduced power consumption and longer battery life for IoMT devices, as well as less congestion for the Wi-Fi network.
- WPA3: Healthcare industry is tasked with protecting critical medical information and patient records by regulatory requirements, especially when such information is transmitted over the air. The latest WPA3 standard offers enhanced security protection and is available in two forms:
- WPA3-Enterprise: Unlike WPA2, WPA3-Enterprise provides a 192-bit security suite, making for a more robust security system for enterprise environments, making critical networks harder for hackers to penetrate.
- WPA3-Personal: WPA3-Personal uses Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE) (RFC 7664) to replace Pre-shared Key (PSK) in WPA2-Personal, to offer forward secrecy, that helps protect data traffic by making it resistant to offline dictionary attacks.
In addition, Wi-Fi 6 is backward compatible, enabling legacy clients to co-exist with the latest Wi-Fi 6 devices. This is particularly important in healthcare facilities, where thousands of devices from various Wi-Fi generations are served by the same network at any given time.
In the sequel to this blog, we will take a closer look at Wi-Fi device and network testing considerations for healthcare providers.

